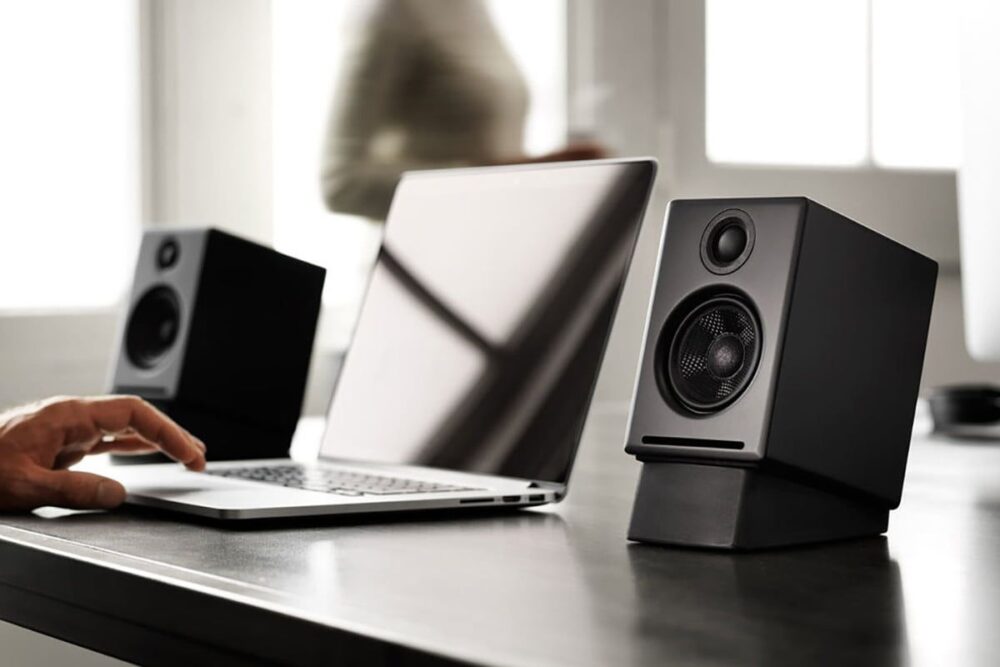
Speakers, those seemingly unassuming devices we encounter in our daily lives, hold a far more intriguing story than one might imagine. They are not merely components that emit sound; they are the portals that connect us to the auditory universe of music, dialogue, and ambient noise. This deep dive into the realm of speakers will unravel the intricacies of how they function, their journey through time, how we assess their quality, and why they are an indispensable part of our interaction with computers and digital devices.
How do Speakers Work?
Speakers are marvels of engineering, transforming electrical signals into the symphony of sounds that surround us. Let’s break down the essential components and the mechanics of how they operate:
1. Diaphragm: At the heart of every speaker is a diaphragm, typically made of materials like paper, plastic, or metal. This diaphragm is attached to a coil of wire.
2. Magnetic Field: Surrounding the coil is a magnet. When an electrical current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field.
3. Movement and Vibration: The interaction between the magnetic field and the coil causes the diaphragm to move back and forth rapidly.
4. Sound Projection: The diaphragm is connected to a cone or dome-shaped structure that serves to amplify and project the sound waves created by its movement.
5. Sound Waves: As the diaphragm vibrates, it pushes and pulls on the surrounding air, creating compressions and rarefactions. These alternating pressure waves are what we perceive as sound.
This process occurs rapidly, with the diaphragm vibrating thousands of times per second to reproduce a wide range of frequencies and create the rich auditory experiences we enjoy.
Evolution of Computer Speakers
The history of computer speakers mirrors the evolution of computing itself. In the early days of computers, audio output was rudimentary, limited to basic beeps and tones used for system alerts. However, as computers transitioned from business tools to multimedia and gaming devices, the demand for better audio quality grew.
The Multimedia Revolution
With the advent of multimedia computing in the late 1980s and early 1990s, computers began to support audio playback, and users wanted better sound quality. This led to the development of dedicated computer speakers, often featuring built-in amplifiers to enhance audio fidelity.
Gaming and Surround Sound
The rise of computer gaming further fueled the demand for high-quality audio. Gamers sought immersive experiences with surround sound systems and subwoofers, creating a market for specialized gaming speakers.
Integration and Portability
In recent years, many computers come with integrated speakers, and laptops often have built-in audio systems. Additionally, portable and Bluetooth speakers have gained popularity, allowing users to take their sound experience on the go.
Rating a Speaker: What Matters?
Evaluating the quality of a speaker involves considering several key factors:
1. Sound Quality: Sound quality encompasses factors such as clarity, fidelity, and the ability to reproduce a wide range of frequencies accurately. A high-quality speaker delivers clear and well-balanced audio.
2. Power (Wattage): The power rating of a speaker, measured in watts (W), determines how loud it can get. Higher wattage generally results in a louder and more dynamic sound.
3. Frequency Response: A speaker’s frequency response indicates the range of frequencies it can reproduce. A broader frequency response allows for more accurate audio reproduction, capturing both low and high tones.
4. Impedance: Impedance, measured in ohms (Ω), affects how well a speaker can interface with an amplifier. Matching impedance levels is essential for optimal performance.
5. Sensitivity: Sensitivity, measured in decibels (dB), indicates how efficiently a speaker converts electrical power into sound. Higher sensitivity often means better performance with less power.
The Necessity of Computer Speakers
Why do we Need Computer Speakers?
Computer speakers fulfill various vital functions in our digital lives:
1. Audio Output: They serve as the primary means for us to hear audio content from our computers, whether it’s music, videos, games, or voice calls.
2. Enhanced Multimedia: Quality speakers significantly enhance multimedia and gaming experiences, providing immersive soundscapes that complement visual content.
3. Communication: Whether it’s online meetings, video conferencing, or virtual gatherings, clear and audible communication relies on speakers, whether built-in or external.
4. Accessibility: Speakers play a critical role in making digital content accessible to those who rely on screen-reading software or need auditory feedback while interacting with computers.
Speaker Terms and More
To truly appreciate the world of speakers, it’s essential to familiarize ourselves with some key terms and concepts:
Is a Speaker Input or Output?
A speaker is an output device. It takes electrical input signals and converts them into audible output in the form of sound waves.
Who Invented the Speaker?
The invention of the speaker is attributed to Alexander Graham Bell, the famed inventor of the telephone. His work on the telephone led to advancements in the technology of sound transmission and ultimately the development of the speaker.
When were Speakers Invented?
Speakers have a long history, with developments dating back to the late 19th century. However, modern speakers, as we know them today, began to take shape in the early 20th century.
Part of the Speaker
Understanding the anatomy of a speaker can enhance our appreciation of how it functions:
– Voice Coil: The coil of wire attached to the diaphragm.
– Magnet: The magnet that surrounds the voice coil.
– Cone or Dome: The structure connected to the diaphragm that amplifies and projects sound.
– Frequency Range: The range of frequencies a speaker can reproduce.
– Driver: The part of the speaker that moves the diaphragm.
Conclusion
Speakers, often overlooked in their simplicity, are the conduits that connect us to the auditory dimensions of our digital world. As we play music, watch movies, engage in video calls, or immerse ourselves in virtual environments; it’s the speakers that faithfully convert electrical signals into the symphony of sound that enriches our digital lives. They are the silent heroes in our sonic journeys, ensuring that we hear, feel, and experience the world of audio in all its richness.
Understanding how speakers function, how to evaluate their quality, and why they are essential in modern computing underscores their significance. These unassuming devices are not just output mechanisms; they are the architects of our sonic landscapes, shaping the way we interact with digital content.
So, the next time you tap your keyboard, click your mouse or watch a video, remember the speakers that faithfully convert electrical signals into the symphony of sound that accompanies your digital experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does a speaker produce sound?
– Answer: A speaker produces sound by converting electrical signals into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations cause the speaker’s diaphragm to move, creating pressure waves in the air that we perceive as sound.
2. What is the difference between a woofer and a tweeter?
– Answer: Woofers are designed to reproduce low-frequency sounds (bass), while tweeters are optimized for high-frequency sounds (treble). Together, they provide a full spectrum of audio frequencies.
3. Can I connect external speakers to my laptop or smartphone?
– Answer: Yes, most laptops and smartphones have audio output ports that allow you to connect external speakers for better sound quality. You can use Bluetooth speakers or wired connections, depending on your device.
4. How do I assess the sound quality of a speaker?
– Answer: To assess sound quality, consider factors such as clarity, fidelity, frequency response, power (wattage), and sensitivity. Reviews, listening tests, and expert opinions can also help in evaluating a speaker’s performance.
5. Are there differences between computer speakers and home theater speakers?
– Answer: Yes, there are differences. Computer speakers are typically compact and designed for near-field listening, while home theater speakers are larger and optimized for room-filling sound. Home theater systems also often include subwoofers for deep bass.
6. What is the purpose of an amplifier with speakers?
– Answer: An amplifier is used to boost the electrical signal before it reaches the speakers. It increases the power of the signal, allowing speakers to produce louder and clearer sound. Amplifiers are commonly used in stereo systems, home theaters, and concert setups.
Also see: The Top 15 Free Music Download Sites
- How Does Automated Scheduling Save Time and Boost Engagement? - April 16, 2025
- 21 Delicious High Protein Foods - May 31, 2024
- Black Seed Oil: Health and Beauty Benefits - May 30, 2024